串口通信透传转TCP通信
前言
目的:
通过嵌入式通信模块串口通信数据透传转发到网络套接字,实现本地设备联网。
概念:
串行接口是一种可以将接收来自CPU的并行数据字符转换为连续的串行数据流发送出去,同时可将接收的串行数据流转换为并行的数据字符供给CPU的器件;
串口通信(Serial Communications)的概念非常简单,串口按位(bit)发送和接收字节的通信方式;
传输控制协议(TCP,Transmission Control Protocol)是一种面向连接的、可靠的、基于字节流的传输层通信协议。
代码整体结构并不复杂,基本还是C/S架构,暂不考虑通信同步、稳定性、粘包等优化问题,仅完成功能实现。
服务端
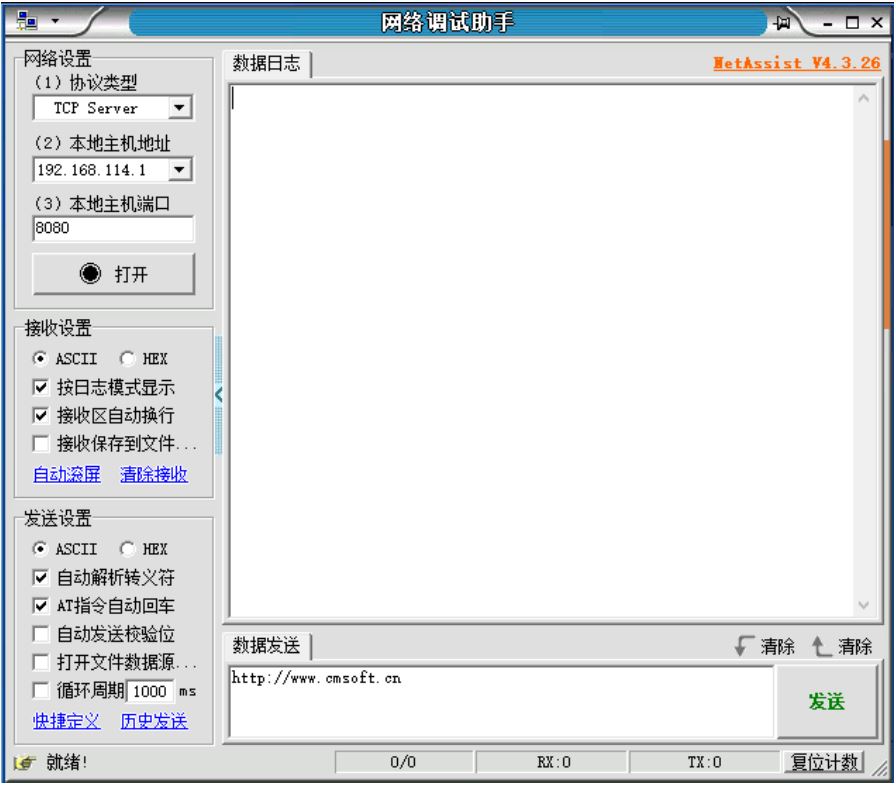
服务端与串口无关,用通用的TCP socket网络通信服务端代码即可。为了方便,这里直接在Windows下载网络调试助手,协议类型设置TCP Server, 自动获取本地IP地址,设置端口,打开后等待客户端连接。
客户端
客户端整体还是串口通信的代码,如下:
com_tcp_client.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#define BUF_LEN_MAX 2048
typedef struct
{
int format; /* 0 ASCII格式; 1 hex格式 */
int debug; /* 0 正常模式, 1 debug模式 */
int com_set; /* 0 原始模式, 1 设置了波特率等的模式 */
}INPUT_PARA_ST;
static INPUT_PARA_ST g_input_para;
#define DEBUG_TO(fmt,arg...) (g_input_para.debug && printf(fmt,##arg))
/**
*@brief 设置串口通信速率
*@param fd 类型 int 打开串口的文件句柄
*@param speed 类型 int 串口速度
*@return void
*/
int speed_arr[] = { B115200,B38400, B19200, B9600, B4800, B2400, B1200, B300,
B115200,B38400, B19200, B9600, B4800, B2400, B1200, B300, };
int name_arr[] = { 115200,38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, 300,
115200, 38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, 300, };
void set_speed(int fd, int speed)
{
int i = 0;
int status = 0;
struct termios option = { 0 };
tcgetattr(fd, &option);
for (i = 0; i < (int)(sizeof(speed_arr) / sizeof(int)); i++)
{
if (speed == name_arr[i])
{
tcflush(fd, TCIOFLUSH);
cfsetispeed(&option, (speed_t)speed_arr[i]);
cfsetospeed(&option, (speed_t)speed_arr[i]);
status = tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &option);
if (status != 0)
{
perror("tcsetattr fd");
return;
}
tcflush(fd, TCIOFLUSH);
}
}
}
int set_databits(struct termios *p_options, int databits)
{
switch (databits) /*设置数据位数*/
{
case 7:
p_options->c_cflag |= CS7;
break;
case 8:
p_options->c_cflag |= CS8;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr, "Unsupported data size\n");
return (-1);
}
return 0;
}
int set_stopbits(struct termios *p_options, int stopbits)
{
/* 设置停止位*/
switch (stopbits)
{
case 1:
p_options->c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
break;
case 2:
p_options->c_cflag |= CSTOPB;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr, "Unsupported stop bits\n");
return (-1);
}
return 0;
}
int set_parity(struct termios *p_options, int parity)
{
switch (parity)
{
case 'n':
case 'N':
p_options->c_cflag &= ~PARENB; /* Clear parity enable */
p_options->c_iflag &= ~INPCK; /* Enable parity checking */
break;
case 'o':
case 'O':
p_options->c_cflag |= (PARODD | PARENB); /* 设置为奇效验*/
p_options->c_iflag |= INPCK; /* Disnable parity checking */
break;
case 'e':
case 'E':
p_options->c_cflag |= PARENB; /* Enable parity */
p_options->c_cflag &= ~PARODD; /* 转换为偶效验*/
p_options->c_iflag |= INPCK; /* Disnable parity checking */
break;
case 'S':
case 's': /*as no parity*/
p_options->c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
p_options->c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
p_options->c_iflag |= INPCK;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr, "Unsupported parity\n");
return (-1);
}
return 0;
}
/**
*@brief 设置串口数据位,停止位和效验位
*@param fd 类型 int 打开的串口文件句柄
*@param databits 类型 int 数据位 取值 为 7 或者8
*@param stopbits 类型 int 停止位 取值为 1 或者2
*@param parity 类型 int 效验类型 取值为N,E,O,,S
*/
int set_data_mode(int fd, int databits, int stopbits, int parity)
{
struct termios options;
if (tcgetattr(fd, &options) != 0) {
perror("SetupSerial 1");
return(-1);
}
options.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
set_databits(&options, databits);
set_stopbits(&options, stopbits);
set_parity(&options, parity);
tcflush(fd, TCIFLUSH);
options.c_cc[VTIME] = 150; /* 设置超时15 seconds*/
options.c_cc[VMIN] = 0; /* Update the options and do it NOW */
#if 0
printf("c_iflag:%x\n", options.c_iflag);
printf("c_oflag:%x\n", options.c_oflag);
printf("c_cflag:%x\n", options.c_cflag);
printf("c_lflag:%x\n", options.c_lflag);
#endif
if (tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &options) != 0)
{
perror("SetupSerial 3");
return (-1);
}
return (0);
}
/*********************************************************************/
int open_dev(const char *Dev)
{
int fd = open(Dev, O_RDWR); //| O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY
if (-1 == fd)
{
perror("Can't Open Serial Port");
return -1;
}
else
return fd;
}
/*
使用原始模式打开串口,主要用于usb模拟出来的串口
*/
int set_com_orginal_mod(int fd)
{
struct termios options;
if (tcgetattr(fd, &options) != 0) {
perror("SetupSerial 1");
return(-1);
}
tcflush(fd, TCIFLUSH);
options.c_iflag = 0;
options.c_cflag = 0;
options.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG); /*Input*/
options.c_oflag &= ~OPOST; /*Output*/
if (tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &options) != 0)
{
perror("SetupSerial 3");
return (-1);
}
return (0);
}
static int para_parse_and_check(int argc, char **argv)
{
int i = 0;
int ret = 0;
if (argc < 2)
{
ret = -1;
}
for (i = 2; i < argc; i++)
{
if (0 == strcasecmp("-x", argv[i]))
{
g_input_para.format = 1;
}
else if (0 == strcasecmp("-debug", argv[i]))
{
g_input_para.debug = 1;
}
else if (0 == strcasecmp("-com", argv[i]))
{
g_input_para.com_set = 1;
}
else
{
ret = -1;
break;
}
}
if (-1 == ret)
{
printf("usage:cometest dev [options]\n");
printf("option:\n");
printf(" -x 使用hex模式 \n");
printf(" -debug 调试模式 \n");
printf(" -com 使用com设置波特率模式 \n");
}
return ret;
}
int set_com_option(int fd, int mod)
{
if (1 == mod)
{
set_speed(fd, 115200);
if (set_data_mode(fd, 8, 1, 'N') == -1)
{
perror("Set Parity Error\n");
return -1;
}
}
else
{
if (0 != set_com_orginal_mod(fd))
{
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
static int write_com_data(int fd, char *buf, size_t len, int format)
{
int write_len = 0;
len = strlen(buf);
if (0 == len)
{
return 0;
}
if (0 == format)
{
DEBUG_TO("ascii:%s", buf);
write_len = write(fd, buf, strlen(buf));
}
else
{
int i = 0;
int target_data_len = 0;
char hex[3];
unsigned int ascii = 0;
char target_data[BUF_LEN_MAX / 2 + 1] = { 0 };
if (len % 2 != 0)
{
perror("input error please input even count\n");
return -1;
}
target_data_len = 0;
for (i = 0; i < (int)len; i = i + 2)
{
hex[0] = buf[i];
hex[1] = buf[i + 1];
hex[2] = '\0';
DEBUG_TO("hex:%s", hex);
sscanf(hex, "%x", &ascii);
DEBUG_TO("=asci%d ", ascii);
target_data[target_data_len] = (char)ascii;
target_data_len++;
}
write_len = write(fd, target_data, (size_t)target_data_len);
}
return write_len;
}
int comtest_process(int fd, int cfd)
{
int select_re = 0;
fd_set read_set, all_set;
int max_fd = 0;
char buff[BUF_LEN_MAX + 1] = { 0 };
int nread = 0;
FD_ZERO(&all_set);
FD_SET(fd, &all_set);
FD_SET(STDIN_FILENO, &all_set);
max_fd = fd > STDIN_FILENO ? fd : STDIN_FILENO;
for (;;)
{
read_set = all_set;
select_re = select(max_fd + 1, &read_set, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (select_re > 0)
{
if (FD_ISSET(fd, &read_set))
{
if ((nread = read(fd, buff, BUF_LEN_MAX - 1)) > 0)
{
int len = send(cfd, buff, strlen(buff), 0);
if (len < 0)
{
printf("msg is:%s,send failer,errno is %d,errno message is:%s\n", buff, errno, strerror(errno));
break;
}
}
else
{
perror("read data error\n");
exit(1);
}
}
if (FD_ISSET(STDIN_FILENO, &read_set))
{
memset(buff, 0, sizeof(buff));
if (0 >= (nread = read(STDIN_FILENO, buff, BUF_LEN_MAX)))
{
perror("read data from STDIN_FILENO error\n");
exit(1);
}
if (0 == strncmp("quit", buff, strlen("quit")))
{
exit(0);
}
write_com_data(fd, buff, strlen(buff), g_input_para.format);
}
}
else
{
perror("select error\n");
break;
}
}
return -1;
}
int client_connect(const char* ip, int port)
{
int err = 0;
int cfd;
struct sockaddr_in c_addr;
unsigned int c_port;
char buf[BUF_LEN_MAX] = { 0 };
//创建socket
if ((cfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0)
{
perror("socket error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//发送连接服务器的请求
memset(&c_addr, 0, sizeof(c_addr));
c_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
c_addr.sin_port = htons(c_port);
inet_pton(AF_INET, ip, &c_addr.sin_addr.s_addr);
if (connect(cfd, (struct sockaddr*)(&c_addr), sizeof(c_addr)) == -1)
{
perror("connect error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("==============================================\n");
printf("connect success!\n");
printf("==============================================\n");
return cfd;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
char *dev = NULL;
int ret = 0;
const char* ip = "192.168.114.1";
int port = 8080;
ret = para_parse_and_check(argc, argv);
if (ret != 0)
{
return -1;
}
dev = argv[1];
fd = open_dev(dev);
if (fd < 0)
{
return -1;
}
if (0 != set_com_option(fd, g_input_para.com_set))
{
close(fd);
return -1;
}
int cfd = client_connect(ip, port);
if (cfd < 0)
{
return -1;
}
comtest_process(fd, cfd);
close(fd);
return -1;
}
编译指令:
gcc com_tcp_client.c -o client
./client /dev/ttyUSB2 -com
简单解释一下。通信模块接入系统后会在/dev目录下映射出ttyUSB0~ttyUSB4五个串口,ttyUSB2为PCUI口,利用该口通信。检查终端命令,打开串口,设置串口属性后进入client_connect函数,与服务端建立连接。在函数comtest_process中,利用I/O多路复用函数select监控串口的文件描述符和标注输入的文件描述符,当在键盘上敲入“hello world”,标准输入事件发生变化,select激活write_com_data向串口写入数据,串口状态发生变化同时也被select感应到,激活send(cfd, buff, strlen(buff), 0),即可在服务端看到”hello world”。
搞定。